What Is A Gastric Balloon?

Are you looking to lose weight but are hesitant to undergo surgery? Then a gastric balloon may be the solution for you. A gastric balloon is a weight loss solution that involves placing a soft, inflatable balloon in the stomach to reduce its capacity and help you feel fuller faster and stay fuller for longer. It is considered safe and a less invasive alternative to weight loss surgery.
How Does the Gastric Balloon Work?
Gastric balloons help reduce physical hunger – they help your body to feel fuller faster and to stay fuller for longer. They also help you to eat smaller portions. How?
When you have a balloon in the stomach:
-
It reduces the amount of space in your stomach for food – you feel full without having to eat as much.
-
Since it takes up space in your stomach – when you eat, a neurohormonal mechanism tells your brain that you have already had enough food – again, that means you feel fuller faster.
-
It takes your stomach about 2 hours longer to empty itself than it would without a balloon.1 This helps you to feel fuller for longer. Research has shown that the longer it takes for food to empty from your stomach (called ‘gastric emptying time’), the better the weight-loss outcome.2
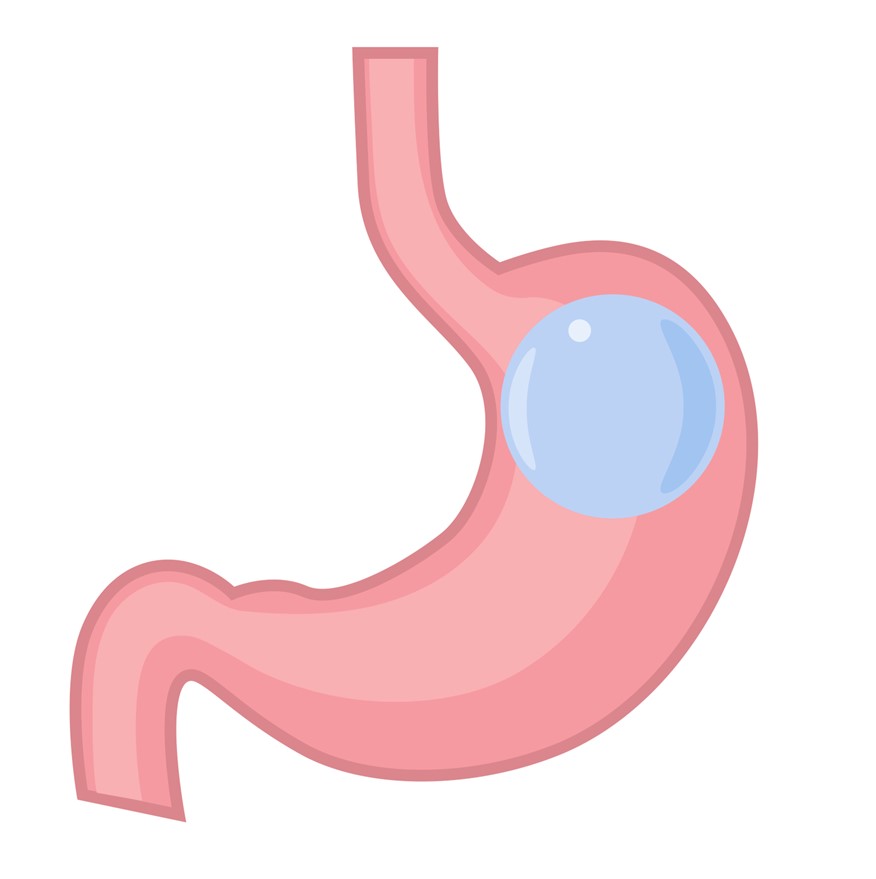
The balloon stays in the stomach for a period of time, usually several months, during which it helps people to eat smaller portions, consume fewer calories, and achieve significant weight loss. After this residence period, the balloon deflates and is removed, and people are advised to continue with a healthy diet and regular exercise routine to maintain their weight loss.
Gastric Balloon vs. Gastric Band vs. Gastric Bypass Surgery vs. Gastric Sleeve Surgery vs Lap-band
Gastric balloons, gastric band, gastric bypass surgery, gastric sleeve surgery and lap-band are all weight loss solutions that can help individuals achieve significant weight loss. However, each procedure works differently and is suitable for different types of people. Weight loss surgery (also called metabolic bariatric surgery, or MBS) involves making incisions in the abdomen to operate on the stomach or intestine.
Gastric band involves placing a band around the stomach to create a smaller pouch, while gastric bypass surgery involves rerouting the intestine to reduce the amount of food absorbed by the body. Lap-band is a type of gastric band that is placed laparoscopically.
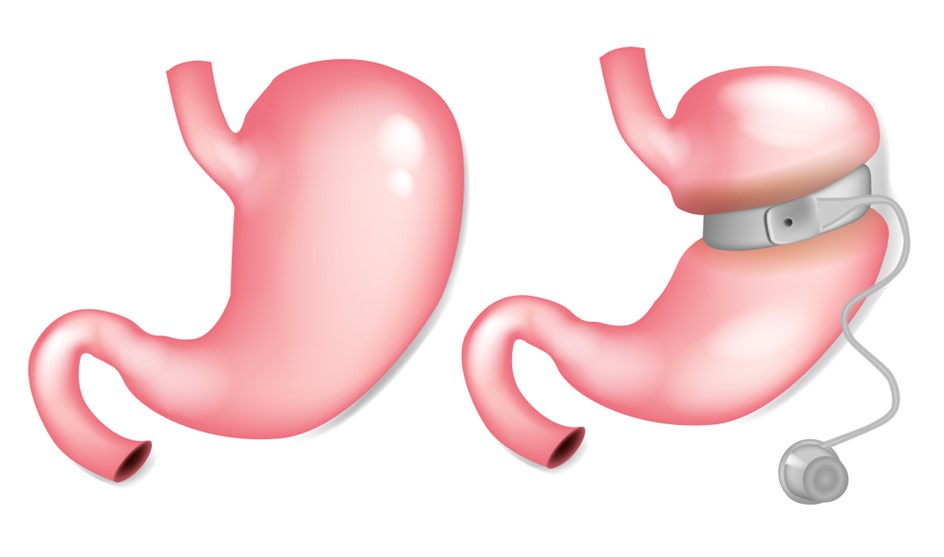
Gastric band surgery
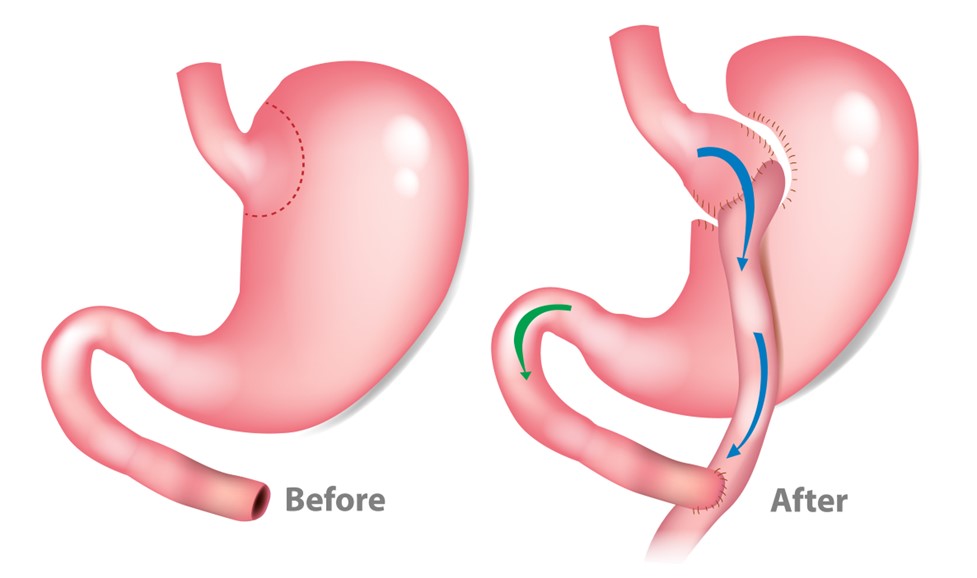
Gastric bypass surgery
We dive deeper into the different types of bariatric surgery here.
In contrast, the gastric balloon is a minimally invasive option that offers a safe alternative for individuals who may not be suitable for surgery due to medical reasons or who prefer a less invasive approach. Unlike surgery, the gastric balloon procedure is reversible and is removed after its intended stay in the stomach.
Comparison between Gastric Balloon and Weight Loss Surgery
When considering weight loss options, it's crucial to weigh the potential risks and benefits of each approach. Bariatric surgery is often a major operation that carries the risk of potential complications.
In addition, the permanent changes to the body, the hospital costs and longer recovery time associated with bariatric surgery can be a significant barrier for some individuals.
And if we look at weight loss results for bariatric surgery vs gastric balloons, the 12- to 18-month Allurion Program (which involves two consecutive Allurion Gastric Balloons) stands out as a promising option for weight loss. The program has been shown to deliver weight loss results similar to those of bariatric surgery at one year.4

Benefits of the Gastric Balloon
There are several benefits to choosing non-surgical weight loss options like the gastric balloon. Firstly, one major advantage is the reduction in risks associated with invasive weight loss surgeries and the accompanying costs of hospital stays.
Additionally, gastric balloons are reversible, meaning they can be removed at any time without the need for major surgery. Unlike surgery, gastric balloons are designed to be temporary. They do not alter the shape or size of your stomach or result in any permanent changes to your body.
Gastric balloons have also emerged as an effective weight loss option. Total body weight loss (TBWL) following intra gastric balloon therapy ranges between 6-15%, depending on balloon and program type. Additionally, studies indicate that patients who undergo intragastric balloon procedures can achieve about 50% of their target weight loss within the first month after the procedure.4 This suggests that the intragastric balloon can be an effective weight loss option for individuals seeking rapid initial weight loss.
Furthermore, gastric balloon procedures can help individuals develop healthy habits that can support long-term weight loss. By limiting the amount of food that can be consumed at once and the impact on hunger and satiety, the treatment can encourage individuals to eat smaller meals and snacks and focus on responding to feelings of physical hunger and fullness in more helpful ways for the future. Some studies show that placement of gastric balloons in patients with obesity allows for a reduction in the intensity of behaviors such as grazing, emotional eating, craving sugar.5
Types of Gastric Balloons - Allurion, Orbera, Obalon
There are several types of gastric balloons available in the market, each with its unique features and benefits. The Allurion Gastric Balloon stands out as the world's first and only gastric balloon that does not require surgery, endoscopy or anesthesia. It is a swallowable balloon that can be placed in the stomach in a matter of minutes, making it a safer and more convenient option for patients. Orbera and Obalon are other types of gastric balloons that require an endoscopy under anesthesia for placement and removal.
The Allurion Balloon is made from polyurethane, a material that’s much thinner and more flexible than the silicone material in endoscopic balloons like Orbera and Obalon. The Allurion swallowable balloon is averaging 10x less serious adverse events and 7-8x less intolerance than other liquid filled balloons (reference) Unlike endoscopic balloons, the Allurion Balloon, being malleable, flexes and adapts to the shape of your stomach; it is crafted to the shape of the stomach – an oval shape like a grapefruit, with two flat surfaces.6,7
Unlike other gastric balloons that are only a singular device, the Allurion Balloon is part of the Allurion Program, which combines the placement of the balloon with medical support, digital tools, personalized nutrition and behavior change coaching. This holistic approach provides individuals with a complete weight loss solution, addressing not just the physical aspect but also the psychological and nutritional aspects of weight loss.

Patient wearing the Allurion Health Tracker and using the Allurion app
Endoscopy for Gastric Balloon Procedure - What to Expect?
The gastric balloon placement procedure typically takes about 30 minutes and is done under sedation or local anesthesia. The balloon is inserted through the mouth and down the esophagus into the stomach where it is then filled with saline solution. Patients may experience some discomfort, nausea, and vomiting for the first few days after the procedure. However, these side effects usually subside within a week.
Patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for the first few days after the procedure and gradually transition to solid foods over the next few weeks. It is important to follow a healthy diet and exercise routine to achieve optimal weight loss results.
For endoscopically placed gastric balloons, once the treatment duration is complete, patients need to return to the hospital for the same procedure, this time to deflate and remove the balloon from the body.
Swallowable Gastric Balloon Procedure – What to Expect?
With the Allurion swallowable gastric balloon, there is no need for surgery, endoscopy or anesthesia, making it a less invasive and safer option.
During the 15-minute clinic visit, the patient swallows a capsule containing the deflated balloon attached to a thin tube. Once ingested, an X-ray is performed to ensure the capsule is positioned correctly in the stomach.
Next, the doctor will use the tube to fill the balloon with water. This process is carefully monitored, and a second X-ray is conducted to confirm that the balloon is properly filled. Once confirmed, the doctor gently removes the tube, and the procedure is done.
After approximately 4 months, the Allurion gastric balloon self-empties and passes out of the body naturally.
Cost of a Gastric Balloon
The cost of a gastric balloon can vary depending on a variety of factors such as the location of the clinic, the specific type of balloon used, and the extent of the medical services provided. It's important to note that while the initial cost of the procedure may seem high, it may ultimately be a cost-effective solution when compared to the ongoing costs of managing obesity-related health conditions.
However, some clinics may offer financing options to help make the procedure more affordable for those who are interested.
How much does the Allurion Program cost? Find out more here.
Related articles:
References:
1. Vargas EJ, Bazerbachi F, Calderon G, et al. Changes in Time of Gastric Emptying After Surgical and Endoscopic Bariatrics and Weight Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(1):57-68.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2019.03.047
2. Lopez-Nava et al., Obes Surgery, 2020, 30(9): 3347-3353
3. Ienca et al. Sequential Allurion Balloon Treatment 1- Year Weight Loss Results Approximate Bariatric Surgery Results, TOS Obesity Week, 2020
4. Armijo PR, Pokala B, Flores L, Leon MA, Oleynikov D, Kothari V. Patients undergoing intragastric balloon achieve approximately 50% of their target weight loss in the first month postoperatively: an MBSAQIP analysis. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019 Dec;15(12):2060-2065.
5. Genco A, Maselli R, Frangella F, et al. Effect of consecutive intragastric balloon (BIB®) plus diet versus single BIB® plus diet on eating disorders not otherwise specified (EDNOS) in obese patients. Obes Surg. Dec 2013;23(12):2075-9. doi:10.1007/s11695-013-1028-6
6. Taha et al. Obesity Surgery. 2020; 2. Ponce et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015; 3. US FDA Post-Approval Studies Database Application #P140012; 4. Orbera Pivotal Trial NCT00730327; 5. Moore et al., 2020; 6. Allurion Enlighten Trial; 7. Ienca et al. TOS Obesity Week. 2022
7. Jamal MH, Al-Kanawati N, ElAbd R, et al. A Study Examining the Orbera365 Intragastric Balloon Safety and Effects on Weight Loss [published correction appears in Obes Surg. 2022 Feb;32(2):574]. Obes Surg. 2021;31(12):5342-5347. doi:10.1007/s11695-021-05729-8



